Process improvement is the practice of identifying, analyzing, and optimizing existing business processes to enhance performance and ensure continuous improvement.
When process improvement is practiced continuously over the lifespan of a business, it is then referred to as continuous improvement. Continuous improvement is the practice of making incremental changes to business processes over time to improve team efficiency and the quality of products or services offered to customers.
The main goal of process improvement is to reduce waste, improve productivity, streamline existing processes, and reduce errors to implement company-wide change for the better.
Process improvement in business often requires organizations to follow a systematic approach or specific methodology. These methodologies can be modified or combined with other process improvement approaches to create a process improvement plan that fits the unique needs of organizations.
Types of process improvement methodologies
There are a variety of process improvement methodologies that can assist companies in improving their business operations.
Although these methodologies share the common goal of identifying process improvement opportunities and fixing them, each framework has a different structure.
Here are a few of the most common methodologies used by leading businesses to tackle process improvement throughout their organizations.
Kaizen
Kaizen is a Japanese business philosophy that focuses on the continuous improvement of business operations. This philosophy is also the backbone of the lean project management methodology that thrives on respect for people and continuous improvement.
Kaizen aims to eliminate wastefulness, unevenness, and overburden—otherwise known as Muda, Mura, and Muri—to improve business operations.
Kaizen is implemented across a business using a six-step cycle that identifies problems, finds solutions to those problems, tests out those solutions, and analyzes the results of the entire project workflow to aid continuous process improvement throughout the organization.
Six Sigma
This popular process improvement methodology aims to minimize defects and inconsistencies in business processes by using statistical data as benchmarks to help business managers understand if their current processes are properly optimized.
In Six Sigma, a process is considered optimized if it produces less than 3.4 defects per one million cycles. Six Sigma also follows the define, measure, analyze, improve, and control (DMAIC) model to improve the quality of existing processes.
The DMAIC model functions include:
- Define the problem and the objectives to be achieved
- Identify what needs to be improved and how to measure improvement
- Analyze the process and influencing factors
- Implement improvements
- Ensure that improvements are sustainable
By following this roadmap, businesses can quickly identify and address opportunities for process improvement.
Kanban
Kanban is a process improvement technique that relies heavily on visualization of business processes. In Kanban, information about tasks within a process are written on the methodology’s signature Kanban cards and placed onto a board with columns that indicate the point at which tasks are to be performed within a workflow. Cards are then moved to reflect task progression, enabling project teams and leadership to visualize operations and projects as they progress from launch to completion.
Kanban helps businesses uncover how tasks flow through business processes and presents valuable insights into where and how workflows begin to slow down or get clogged up. By visualizing and tracking the flow of a project workflow, project teams are better equipped to simultaneously evolve their current processes as they operate.
Process improvement best practices
Implementing process improvements throughout an organization can be challenging without a clear plan for improvement and employee buy-in. Be sure to follow these best practices when attempting to implement change within your organization:
Identify opportunities for improvement
Before implementing a process improvement plan throughout your organization, ensure that the current processes in action within the company are fully understood. Only then can project teams begin to pinpoint where these processes fail and where they succeed.
To do so, map out the entire project workflow and flag any visible bottlenecks within the process and conduct an in-depth gap analysis. After issues in project workflows have been properly identified, establish a quantifiable goal that aims to solve the issues pinpointed within project workflows.
Quantifiable goals are often referred to as SMART goals, which ensure that each goal set is both quantifiable and achievable. An example of a SMART goal would be “to improve the overall efficiency of operations Line B from a current baseline of 30% to 65% within the next six months to produce the tangible benefits of $10,000”.
Obtain stakeholder buy-in
The employees that carry out the tasks within a workflow should be heavily involved in process improvement initiatives. Remember, stakeholder support is the key to success for any business.
Explain to your team why you are changing the way the company operates and how it will deliver value to the business. Clarify how stakeholders are to be involved in the process improvement journey and motivate them to take ownership of their part in the change.
Map out a process improvement plan
Designing a process improvement plan is crucial when implementing change throughout an organization. Be sure to delineate exactly how your team will evaluate risks and measure the effectiveness of process improvements.
When mapping out a process improvement plan, make sure to always keep the customer in mind, since the changes made will affect customers’ experiences. For instance, if your company plans to make changes to the way they receive customer orders, perhaps by switching product ordering services from an online website to a mobile application, consider how this will affect the satisfaction of both new and existing customers.
Test process improvements and collect feedback
Once you have mapped out a comprehensive process improvement plan, it’s time to implement change. Stakeholders involved in the process improvement planning process should be heavily involved in the rollout.
As these process changes begin, be sure to collect feedback from these stakeholders as this will prove helpful when fine-tuning process improvements. Be prepared to run through a project workflow multiple times with the new process improvements in place. This enables project teams to adjust process improvements as necessary over time.
Monitor and analyze process improvements
Monitoring process improvements after their implementation is a key part of the change process. Continuous workflow optimization requires project teams to move through various iterations of process improvement cycles to meet or exceed set benchmarks.
Each iteration may reveal further issues in the flow of operations that were not addressed in the testing phase of the process improvement cycle. Project teams should expect to not only validate that process improvements are successful but continue to analyze and improve upon them until they are near perfect.
How businesses can benefit from process improvements
All businesses, no matter the industry, rely on process improvement to stay competitive in their respective markets. Here are a few of the benefits that businesses may experience from implementing process improvements within their organization, including:
Reveal hidden bottlenecks
It is difficult for project teams and leadership to identify bottlenecks in key workflows without properly understanding the workflow itself. Process improvements require businesses to assess current workflows and conduct a gap analysis before identifying bottlenecks.
Assessing workflows ensures that process improvement initiatives are aimed at tackling the root of the problem. By thoroughly examining existing company processes, businesses will be better equipped to optimize them and remove obstacles or bottlenecks.
Increase customer satisfaction
Customers expect the companies they interact with to accurately deliver the products and services they value, and in a timely manner. Businesses that do not continuously attempt to improve upon their key workflows risk falling short of customer expectations. This can result in low customer satisfaction and retention rates.
On the other hand, companies that practice continuous process improvement are more likely to fulfill orders on time, provide consistent service, and gain the loyalty of satisfied customers.
Enable company flexibility
Process improvement helps companies get ahead of the competition. Companies that practice continuous improvement are better able to adapt to industry changes while maintaining the quality of products or services offered.
Since process improvement methods often involve the implementation of small changes to key aspects of a given workflow over time, they enable businesses to smoothly adjust their processes as market trends change.
Increase team morale
Work environments that lack process improvement can result in team members feeling unexcited and unmotivated about the work they contribute to the organization. A decrease in team morale is often followed by a decrease in productivity, which can affect a company’s bottom line.
Tedious, unnecessary task fulfillment is bound to drive down morale in the long run. Process improvement eliminates unnecessary work, enabling employees to focus on the critical aspects of their job duties and take pride in their contributions to the company.
Process improvement use cases
Now that we’ve covered the benefits that implementing process improvements can bring to organizations, let’s take a look at how businesses can use process improvement to streamline project workflows and add value to the products and services they offer.
Businesses can utilize process maps to visualize project workflows and identify process improvement opportunities. When looking to streamline business processes, companies must first detail the specific tasks and processes that are currently in place.
To do so, project teams should make use of a process map to review each step of a process and enhance their ability to determine what must be done to optimize operations. Process maps can also be used as learning tools to train new employees since they include detailed accounts of business processes.
The following image depicts a variety of MindManager® process map templates. Process map templates come in various forms; however, they depict process functions similarly.
Radial maps, concept maps, Kanban boards, and time maps are all examples of process maps that can be used to break processes down into individual tasks and determine which tasks need to be altered to aid process improvement.
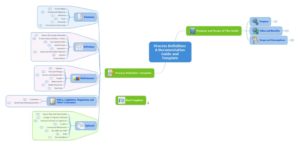
Example Process Map created with MindManager.
Companies can also create workflow diagrams to better visualize and understand the fine details of their business operations. Workflow diagrams are valuable visualization tools that help organizations better understand and keep track of the various tasks within a workflow or process.
These diagrams provide project teams with an overview of everyday company operations to help them identify opportunities for process improvement. Not only do workflow diagrams serve as helpful visualization tools, but they also provide the necessary documentation for legal and regulatory compliance.
Below is an example of a MindManager flowchart, a type of process map that presents each step of a process. Flow charts can be used to identify successful and unsuccessful pathways within a process. With this information, project teams can alter or eliminate tasks that complicate the process.
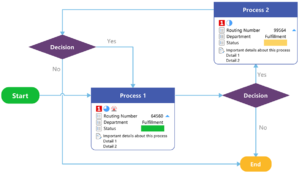
Example flowchart created with MindManager.
Improve your process improvement efforts with MindManager
Businesses must be able to properly visualize each phase of a project’s lifecycle in order to identify opportunities for process improvement. Without workflow visualization tools, project teams will have a hard time understanding what bottlenecks exist within current company operations and how to address them.
MindManager is a mind mapping solution that helps organizations visualize key workflows and test out process improvement initiatives in real time. With MindManager, users can customize templates for process maps and workflow diagrams to create a visualization technique that works best for their organization. You can utilize MindManager’s drag-and-drop functionality to rearrange your designs and add information to the pre-built templates to create the most relevant and useful diagrams for your organization.
MindManager also aids the implementation of process improvements across company departments by enabling users to collaborate on process maps and workflow diagrams in real time. Multiple users can edit existing mind maps at the same time, streamlining company process improvement planning and testing activities.
Discover how visualization with tools like MindManager can enhance process improvement efforts.

