By: Leanne Armstrong
Proven project management methodologies take many forms: from standardized, traditional procedures, to practical philosophies guaranteed to perk up project outcomes.
Some examples of project management methodologies include:
- Waterfall
- Agile
- Scrum
- Lean
- Kanban
- Lean Six Sigma
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
Not every system will suit every project – nor every organization, for that matter.
But as you make your way through this roundup of the most effective project management methodologies, remember that the more principles and practices you keep in your toolbox, the more options you’ll have for meeting project objectives.
[Free eBook] The Ultimate Guide to Visual Project Planning
Why consider established project management methodologies?
Using a well-tested set of guidelines to manage your project ensures you’ll achieve the outcomes you want, consistently and predictably.
Proven project management methodologies come with many benefits:
- They strengthen project planning, keeping your team on point throughout their assignment.
- They help resolve current problems faster and prevent future problems from gaining a foothold.
- They allow you to manage project resources – and by extension your stakeholders’ expectations – more diligently.
Choosing the management approach that best suits your assignment is important. Not only will it influence how you and your team work and communicate together, it will go a long way toward determining your success in meeting specific project deliverables.
So to help you find just the right fit, we’re going to spend a few minutes comparing and contrasting some of the most established project management methodologies.
Project management methodologies comparison
Some project management methodologies aren’t so much scripted management plans as they are a set of organizational values and project best practices.
No matter the form they take however, each of the project management methodologies and examples outlined below boasts a proven track record for keeping teams aligned and maximizing project value.
Let’s compare six of the most popular project management methodologies.
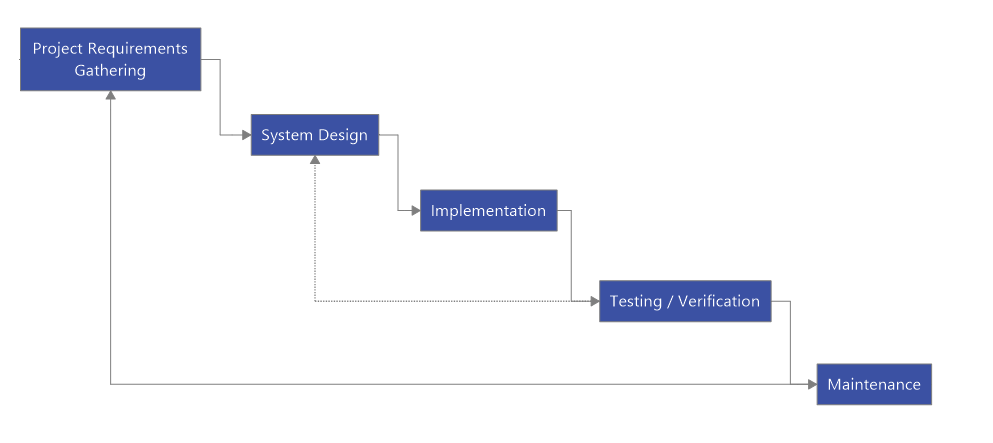
1. Waterfall
What is is?
A straightforward and linear methodology based on solid planning and a once-through approach to project execution.
How it works:
A straightforward and linear methodology based on solid planning and a once-through approach to project execution.
Key benefit:
Improves project results by providing a predictable scope, timeline, and budget.
Example of usage:
Waterfall project management methodologies are ideal when:
- your project is short,
- job requirements are clear and fixed, and
- any technology involved is well understood by your team
This approach is especially suited to construction, manufacturing, and other highly structured projects that are too costly to accommodate changes on the fly.
Here’s a diagram created using MindManager that illustrates the common steps to a waterfall workflow:
 2. Agile
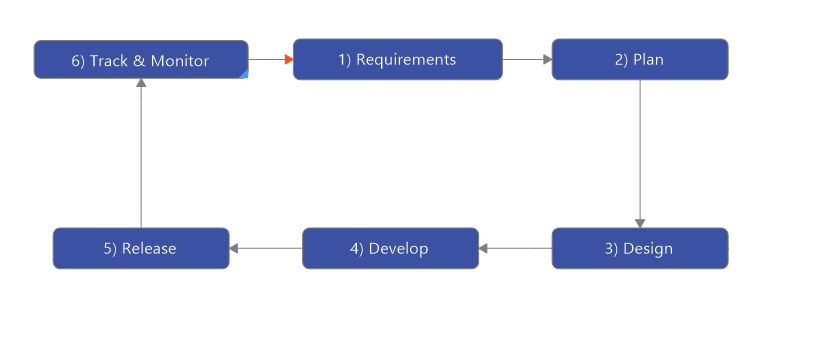
2. Agile
What is is?
A fast, flexible, and collaborative approach to project management, driven by self-organization across teams (or pretty much the opposite of Waterfall).
How it works:
More a philosophy than a pre-planned process, Agile projects are characterized by:
- a series of tasks that are adapted as the demands of a project unfold,
- ongoing communication among team members, and
- regular exchanges between teams and project stakeholders
Key benefit:
Helps your team respond effectively to project unpredictability.
Example of usage:
Although its roots are in software and game development, you can use Agile project management methodologies to:
- innovate in any dynamic industry (think food, clothing, computers, vehicles, music), or
- carry out projects in areas that benefit from highly responsive schedules (like marketing or talent acquisition, for example)
Here’s an example of the agile project management methodology workflow created using MindManager:
 3. Scrum
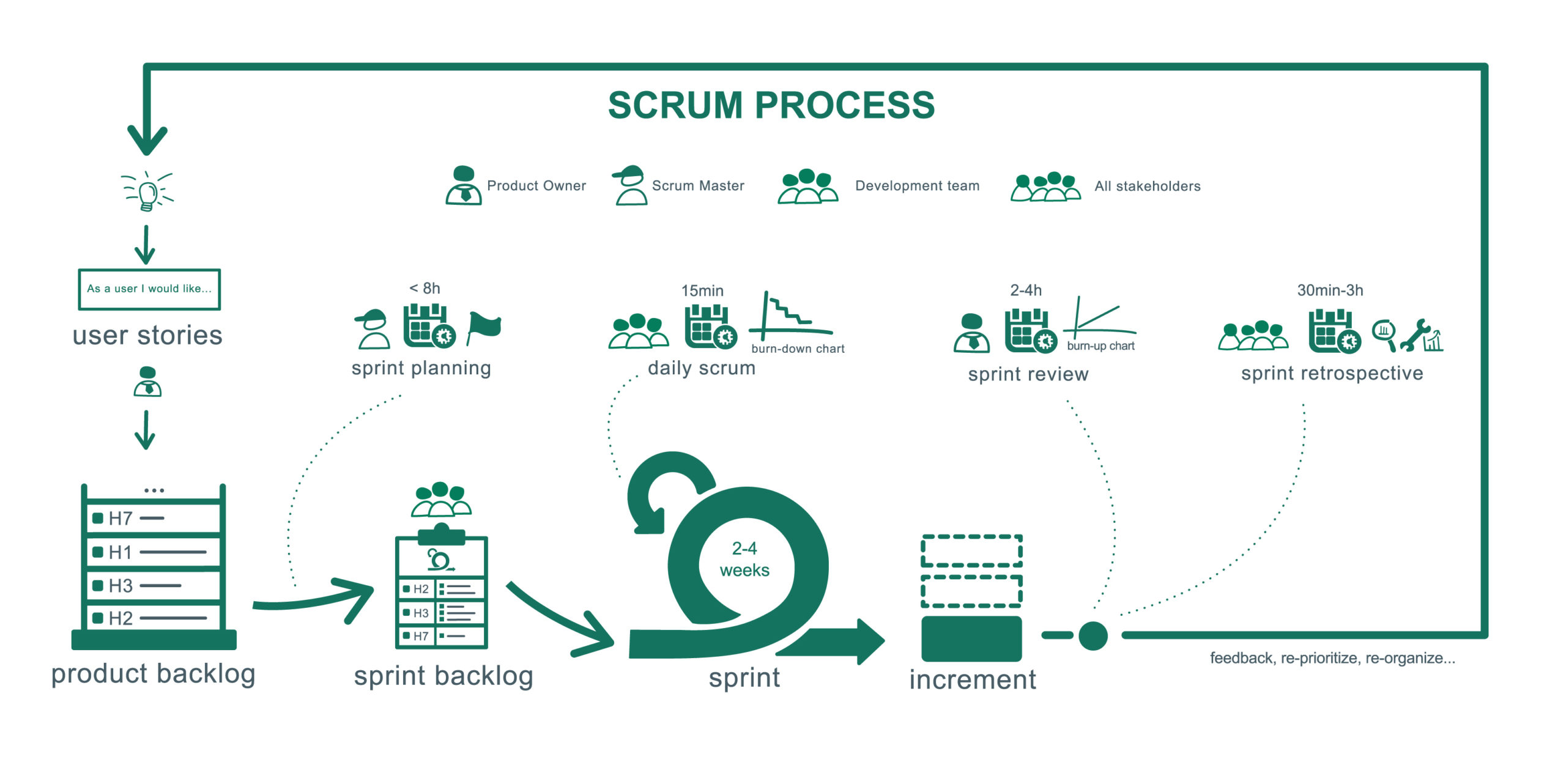
3. Scrum
What is is?
A short, sprint-based methodology that improves teamwork and communication while speeding up product development or project delivery.
How it works:
As Scrum master, you lead a small, self-managing, cross-functional team of no more than 10 people through sprint cycles of 2 – 4 weeks. During these intense development phases, you hold brief, daily Scrums (meetings) where your team reports on progress and holdups. Each sprint session ends with a meeting where team members and project stakeholders review work completed, and decide if it ticks all the boxes on your DoD (Definition of Done) checklist.
Key benefit:
Ideal for helping smaller teams make the most of an Agile project framework.
Example of usage:
Originally (and unsurprisingly) created for software development, you can adapt Scrum project management methodologies to any mission requiring a certain amount of flexibility – like event planning or retail logistics, for example.
Here’s an overview of what a Scrum Process might look like, courtesy of Shutterstock.
 4. Lean
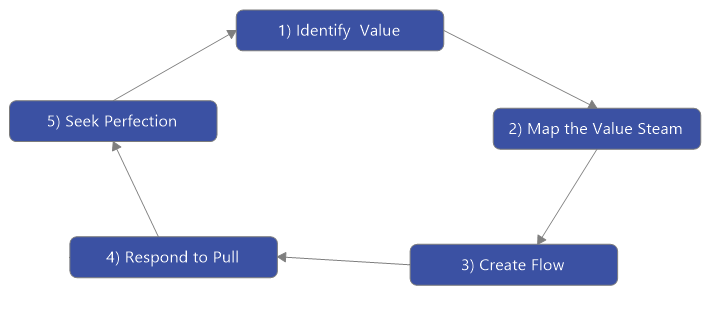
4. Lean
What is is?
A workflow philosophy driven by efficiency and elimination of waste.
How it works:
By thoroughly examining each of the activities in your project workflow, you and your team can determine the minimum amount of resources required to achieve your objectives. The idea is to analyze every step in a process so you can increase result value by eliminating inefficiencies associated with “the way it’s always been done”.
Key benefit:
Lean tools and techniques help keep your project schedule and budget in line.
Example of usage:
Henry Ford’s automated vehicle production workflow is one of the earliest examples of Lean project management. In addition to manufacturing, Lean is ideal for improving project outcomes in construction, education, software development, and any other initiative geared toward an end user.
Here’s an example of the Lean project management methodology workflow, created using MindManager.
 5. Kanban
5. Kanban
What is is?
A visual approach to project management that emphasizes Lean principles and task prioritization to match work-in-progress with team capacity.
How it works:
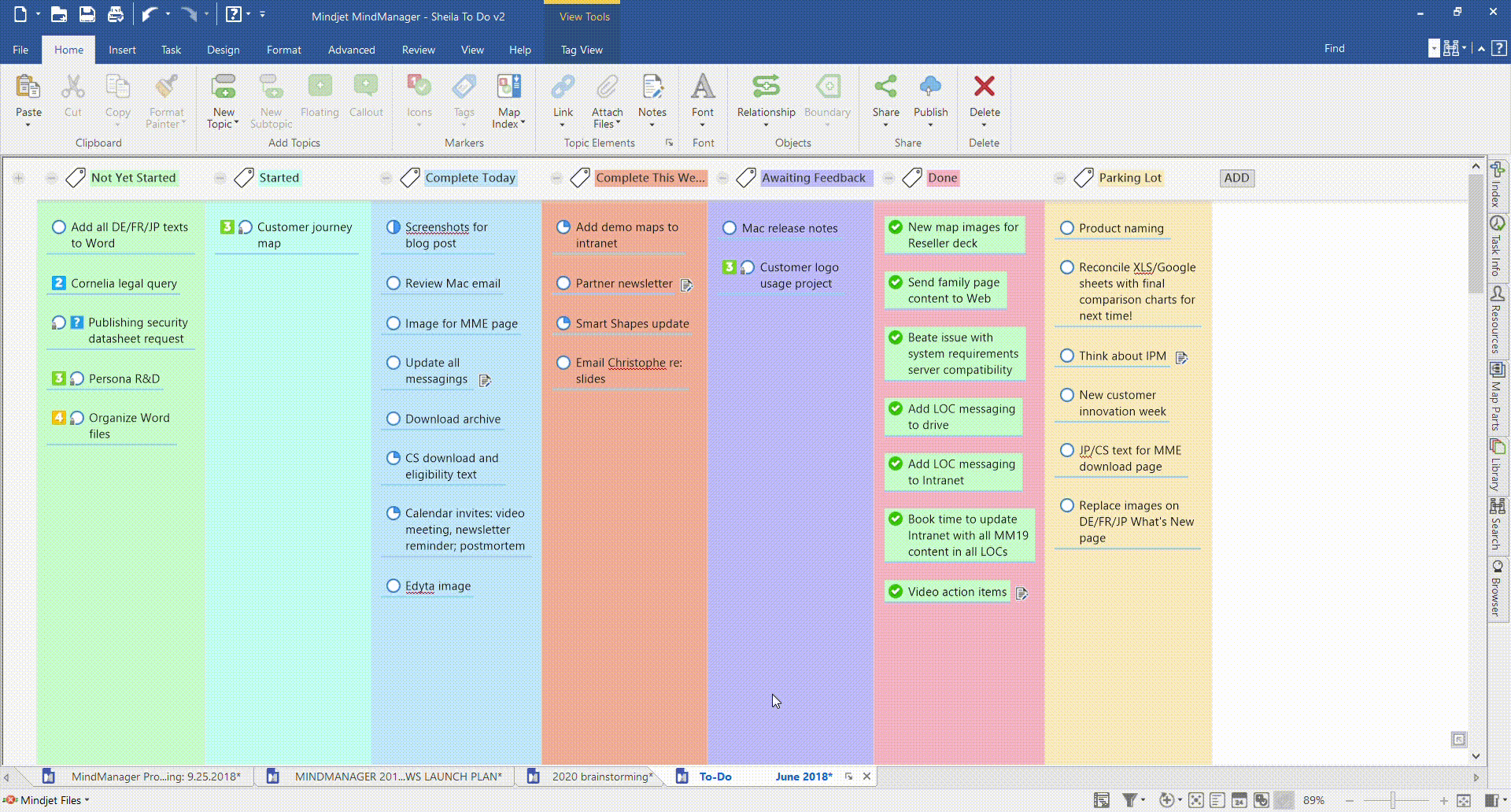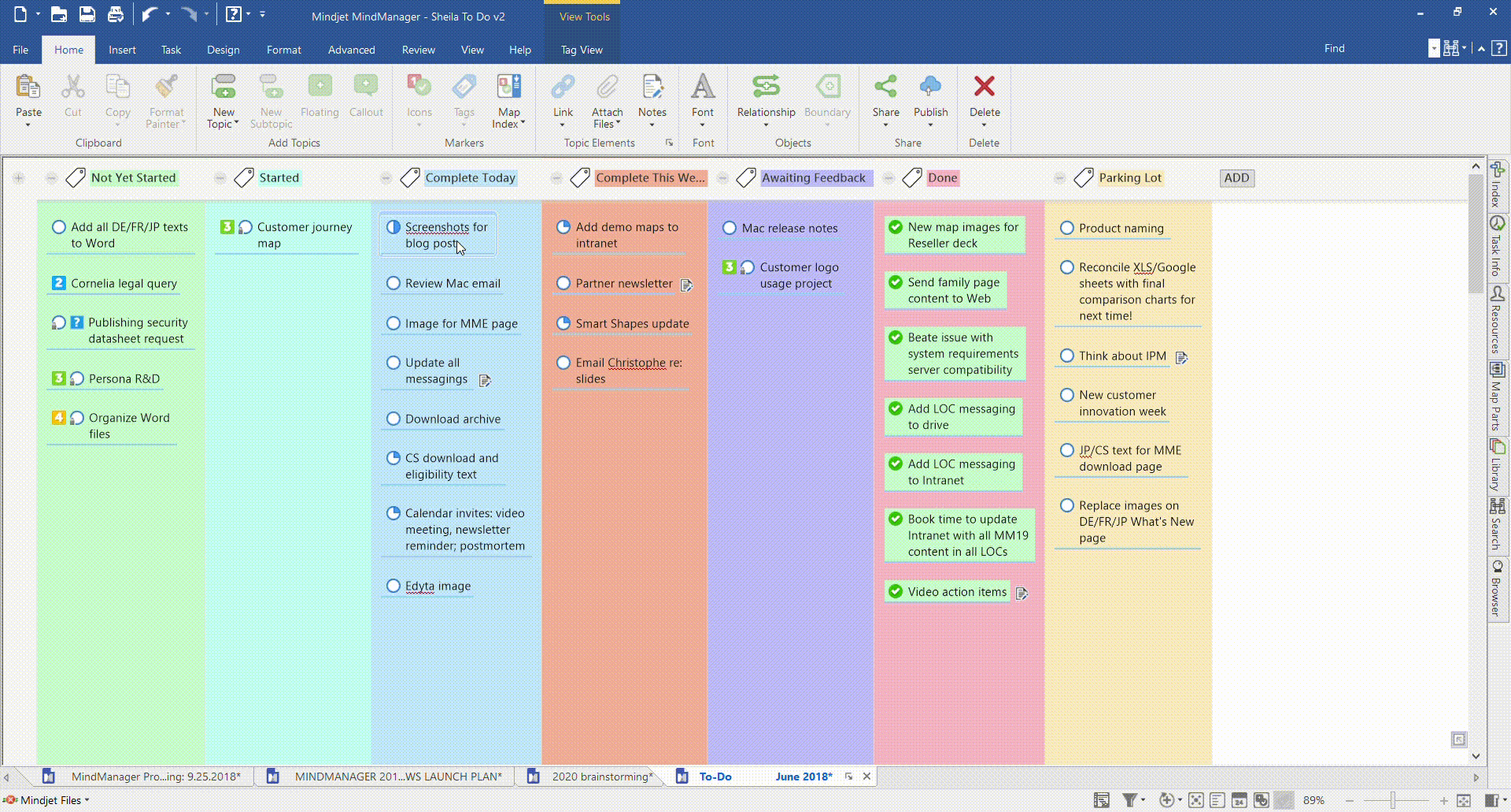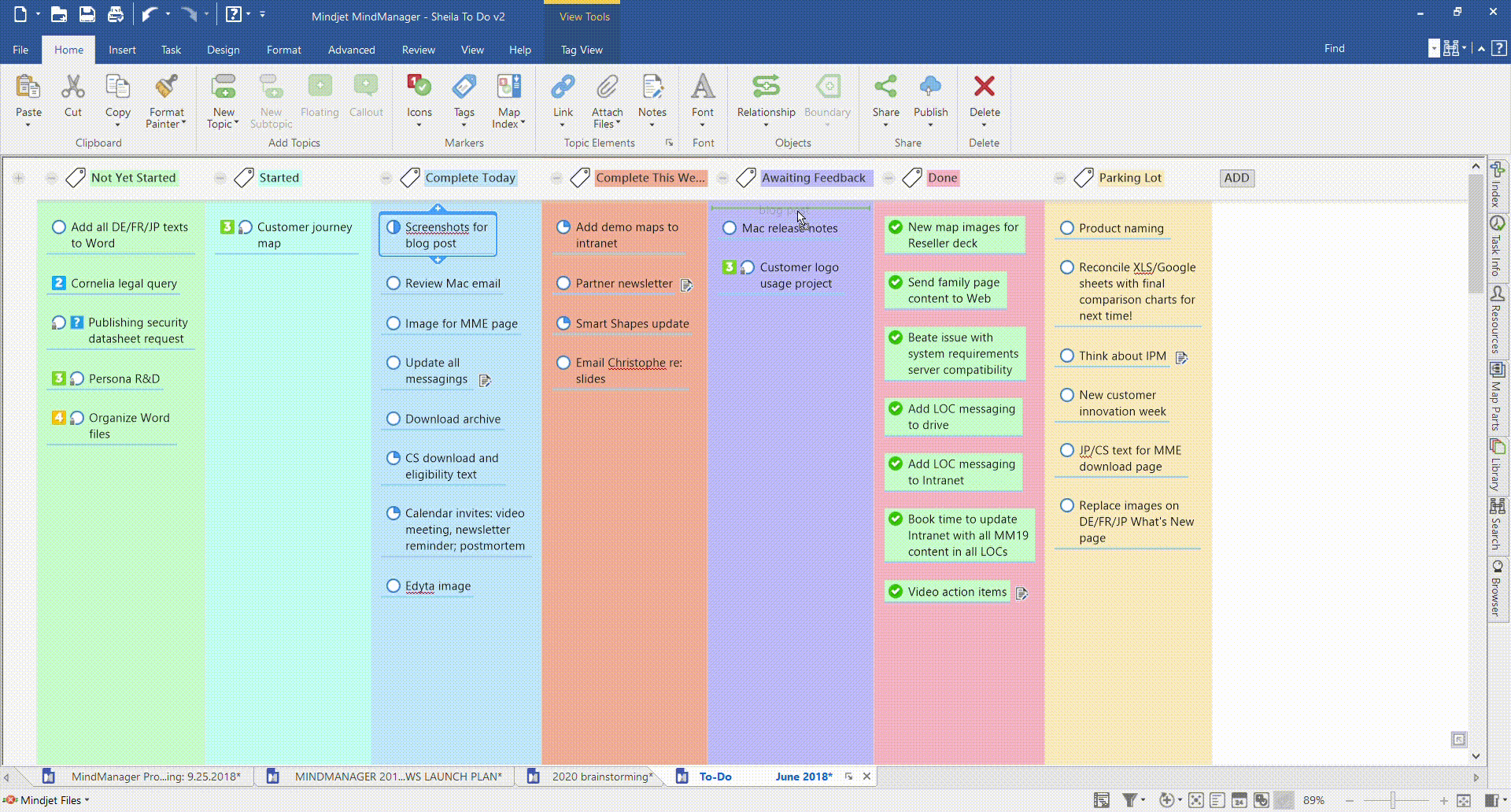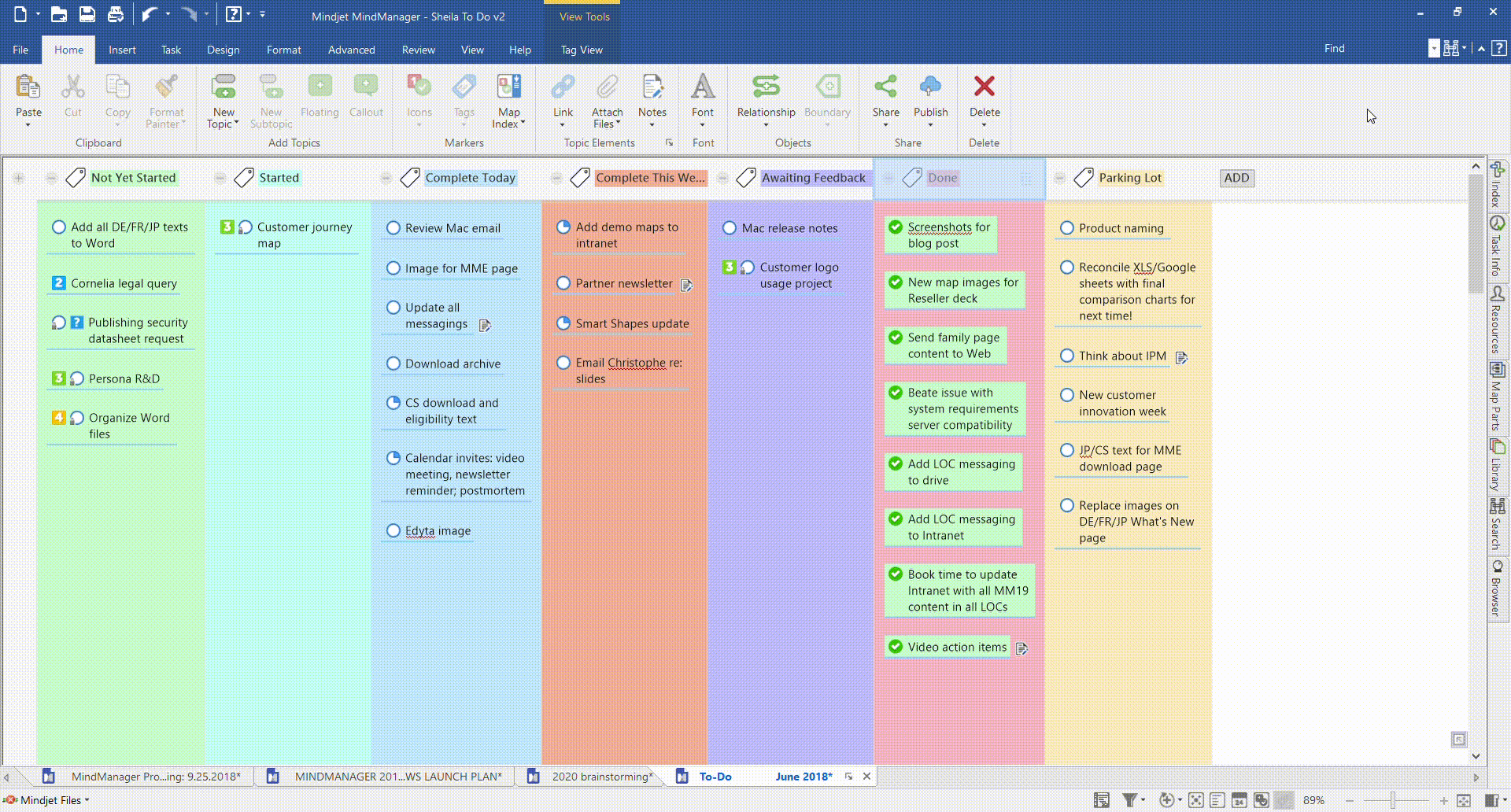
Your team breaks out individual project tasks and places them on a columned Kanban board. The columns can be labelled to suit your project, but are often as simple as “To Do”, “In Progress”, and “Done”. As each task is completed, it’s moved from one column to the next, giving every team member a clear view of workflow and progress.
Key benefit:
Visibly sharing and moving tasks forward encourages collaboration and improves throughput by allowing project activities to evolve on the go.
Example of usage:
Toyota created Kanban project management methodologies to improve efficiency by using vehicle demand to control production. Manufacturing aside, Kanban is great for keeping teams focused on what matters most in any operational, production, or support project that demands steady output in the face of frequently changing priorities.
Here’s an example of a Kanban workflow using MindManager’s Tag View and SmartRules™ features.
6. Lean Six Sigma
What is is?
A collaborative strategy that combines Lean’s waste reduction principles with Six Sigma’s focus on consistent results.
How it works:
You select a team of specialists, then systematically scrutinize project activities and processes with an eye to:
- identifying what isn’t working,
- reducing waste, and
- increasing workflow
The goal is to minimize variations in output so you can stabilize outcomes and maximize the overall quality of your project results.
Key benefit:
Not only does Lean Six Sigma help define and improve processes in a project environment, it can serve as a framework for change at the organizational level.
Example of usage:
Because they improve performance and efficiency metrics, Lean Six Sigma project management methodologies can benefit any project. They’re especially well-suited to maintenance and manufacturing, but can help streamline everything from quarterly forecasting to turnaround times for customer quotes.
Here’s an example of the Lean Six Sigma workflow – based on the DMAIC methodology – created using MindManager.
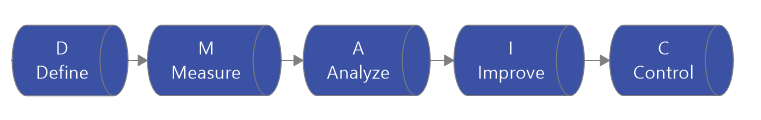 7. Critical Path Method (CPM)
7. Critical Path Method (CPM)
What is is?
A task-driven approach to determining the most efficient path to project execution and closure.
How it works:
Use a visual work breakdown structure (WBS) to build out a model of your project by:
- listing all required tasks and their durations,
- establishing any task dependencies, and
- mapping out each task milestone and project deliverable on an interactive timeline
Reviewing this data will highlight your project’s critical path (the longest stretch of dependent tasks), and allow you to identify those activities with more timing flexibility.
Key benefit:
Lets you take advantage of versatile, visual project management software like MindManager to run projects of all sizes.
Example of usage:
Because it’s driven by detailed planning and a repeatable WBS template, CPM can improve all types of projects by preventing the missed deadlines that stall progress. Use it to create accurate resource estimates for your individual or group assignment.
Here’s a simple diagram illustrating the CPM project management methodology, created using MindManager.
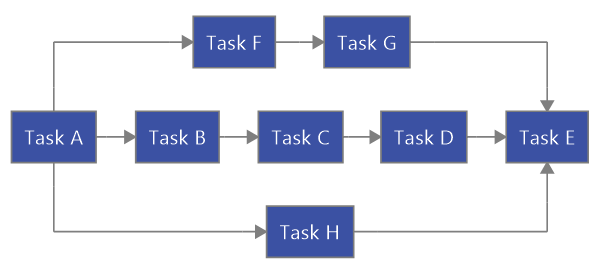
Along with a good team and the right tools, the project management methodologies we’ve introduced here are sure to help you run your next project more efficiently. They yield even better results, however, when you put them to work with the help of project management visualization software like MindManager.
MindManager arms you with a wide range of workflow templates, timeline tools, and brainstorming maps that coordinate team solutions and prevent project roadblocks.
Whether yours is a smaller assignment or a complex initiative, MindManager can help you bring out the best in whichever project management methodology you use to kickstart your project.
Related articles
- Getting back to the basics of project management
- 5 stages of the project management process
- What project management tools should every business be using?
- Your guide to making the most of project management flowcharts
- 5 steps to better project management visualization
- Gantt chart project management: getting back to the basics
 The Ultimate Guide to Visual Project Planning
The Ultimate Guide to Visual Project Planning
Download this free eBook to get a primer on the concept of visual project planning, an exclusive Project Planning Visualization Toolkit, and 13 downloadable visual project planning templates to get you started right away!