A business process is any activity that has a purposeful organizational goal, is highly specific, and produces consistent outcomes. Business processes may be operational, managerial, or supportive.
Operational business processes are the core activities that generate revenue and deliver value to customers, such as developing and delivering your organization’s products and services. Management processes are goal-oriented and drive your business functions, such as task coordination, employee training, budgeting, and team motivation.
Supportive processes are not directly connected to your products or services; rather, they help facilitate smooth operations within the organization. Departments such as accounting, human resource management, and IT are all examples of supportive processes.
Business process improvement (BPI) helps company leaders analyze their organization’s processes to identify ways in which they can improve their accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness. For example, a BPI initiative can produce more efficient workflows and drive business growth by pinpointing opportunities to make improvements or additions to operational procedures, employee skills, or available technologies.
The primary goal of business process improvement is to upgrade the performance of your formal and informal organizational processes. By identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and other process-related issues, organizations can accomplish the following:
- Eliminate redundant processes, which are unnecessary tasks that do not serve a specific purpose.
- Ensure compliance with applicable rules and regulations.
- Reduce errors and unnecessary costs.
- Improve the quality of your products and services.
- Meet customer demands and business goals.
In this post, we will examine the importance of BPI plans, how business process improvement helps identify and evaluate inefficiencies in your company’s business processes, how to implement BPI in your organization, and how to use MindManager® and its visual tools to enhance your BPI strategy.
Why does your company need business process improvement?
Obsolete, inefficient processes stagnate business growth. By finding and fixing bottlenecks, you can cut costs , increase operational productivity, and drive organizational success. When you question and assess the manner in which processes are carried out, you can then determine ways to simplify and redesign how things get done.
Within an organization, every department, team, person, and function might have their own set of processes. If you do not analyze the efficacy of these processes, it could negatively affect the company’s growth and performance. Signs that your company would benefit from implementing business process improvement strategies include the following:
- Processes are non-repeatable. If setbacks require you to go back and recreate processes, there is room for improvement. The best processes are a standardized set of activities, actions, and participants with the goal of producing the same outcome each time.
- Process knowledge and information is deficient. If employees do not understand how processes occur and what the expected outcome is, they will not execute the steps involved in the process correctly. This can cause operational gaps and lost revenue.
- Inconsistent outcomes impact customer satisfaction. Processes that deliver inconsistent outcomes need to be improved in order to generate value for your customers. Customer criticism, redundant tasks, and a lack of control over process standards are all signs that there is room for improvement.
To increase the effectiveness of their business operations, many organizations use business process mapping. This type of mapping generates a visual diagram of the steps within a business process so that everyone understands how the company’s business processes work.
Process mapping is key to identifying where the bottlenecks occur. Creating a flowchart makes it easy to determine the importance of each step involved in your organization’s processes and subprocesses, as well as identify inefficiencies or unnecessary steps.
For example, a business process map can highlight repetitive tasks that waste employee time. If you invest in technology that automates or streamlines these tasks, people will have more time to focus on more impactful work activities.
You can map business processes using paper or a white board, but collaborative visualization tools like MindManager can help take things to the next level. With a variety of adaptable templates, you and other users can easily create, edit, and share diagrams that enable the improvement and optimization of your business processes.
How to set up business process improvement for your organization
Business process improvement streamlines and optimizes processes with the aim of enhancing business operations. There are various methods used to implement BPI plans, but they share the following general steps:
1. Create a sense of urgency. When making a case for a process change, it is important to help others understand the need for change and communicate the importance of taking prompt action. For example, you can identify potential threats and the repercussions of not implementing BPI, as well as examine the opportunities that may arise by improving business processes. These discussions help others assess the prevailing issues and garner the support of key stakeholders.
2. Create a BPI team. No one person can single-handedly lead the change effort. Instead, it takes a team of individuals to develop the strategy to drive business process improvement. The process improvement team could consist of a process owner, a team leader, and key stakeholders who are directly or indirectly involved with the selected process. This team then works together to identify opportunities for enhancement, analyze the challenges within existing processes, and implement improvements.
3. Identify the process you want to improve. The next step in a BPI strategy is to define what you want to improve within your organizational processes. Get input from people who deal with the process regularly to uncover sub-steps that might not be immediately obvious to outside users. Use diagrams such as a flowchart or swim lane diagram to visualize the process and associated responsibilities of various individuals or departments. Once you have mapped out the business process, evaluate the diagram to identify pain points within the system, such as bottlenecks, redundancies, and other inefficiencies.
4. Redesign the process. Once the BPI team has identified underlying issues that impact a particular business process, they can then begin brainstorming solutions to eliminate such problems. For example, you could purchase and deploy new technology to eliminate repetitive tasks or invest in employee training to further their capabilities and therefore your company’s output. The ideal way to redesign a business process is to focus on optimizing any step that provides value while eliminating any wasteful or unnecessary activities.
5. Start small and celebrate often. When initiating a business process improvement plan, start small and focus on incremental changes to help keep people motivated without feeling overwhelmed by the change efforts. Recognize and celebrate those in the organization who are supporting the change process and making process improvements. Improving business processes can be challenging, so recognizing these early wins will help people maintain enthusiasm rather than resist change.
How to use MindManager to facilitate business improvement methodologies
Like project management methodologies, there are numerous options available to organizations that want to improve their business processes. These methodologies vary in how they identify, analyze, and invoke changes, but each has the same end goal of enhancing organizational efficiency.
Some common business process improvement methodologies include the PCDA cycle, Lean Six Sigma, and Kaizen. We will examine each of these in more detail and explain how you can use MindManager’s visual diagramming tools to implement them within your organization.
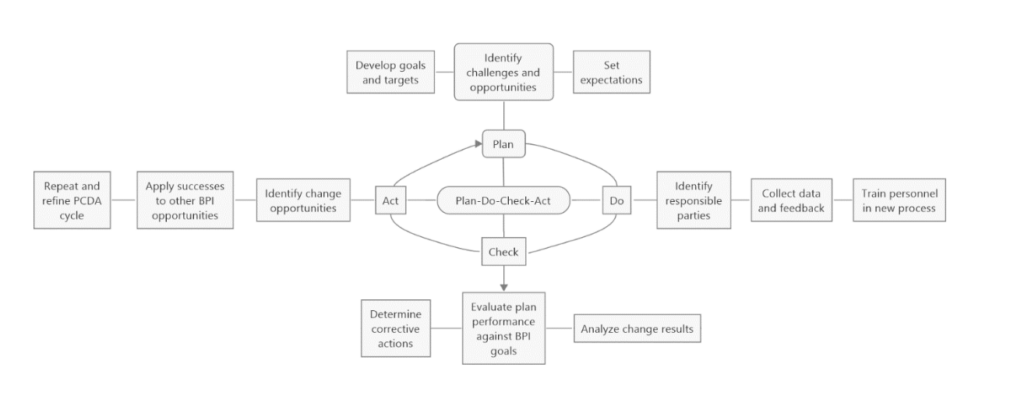
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PCDA)
Organizations looking to implement continuous improvement for business processes do so using the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) framework. The PDCA model helps you improve and change processes at all levels by identifying and resolving inefficiencies that hinder productivity.
When developing a new or improved business process, the PDCA procedure includes four critical components:
- Plan. Identify a process that needs improvement or other opportunities for change. Set goals and targets and communicate the change strategy throughout the organization.
- Do. Put your plan into action and test its effectiveness in improving business processes by collecting data and insights for analysis and evaluation.
- Check. For alignment with the vision and goals of your BPI efforts, it is important to regularly evaluate the results of your plans and tests.
- Act. Use what you learned from those plans and tests to take corrective action where needed and incorporate successful efforts into additional process changes.
With numerous customizable templates available, you have several options when it comes to designing a PDCA cycle in MindManager. You can also use different mind maps for the individual components of a PDCA strategy. For example, during the Plan phase, you can use a strategy map to brainstorm and define your goals, targets, and associated key performance indicators (KPIs).
Lean Six Sigma
The Lean Six Sigma methodology relies on data and statistics to redesign processes. This both increases operational performance and decreases process variations that could otherwise impact the quality of your products or services.
The “lean” designation stems from combining the Lean workflow philosophy’s process of waste elimination with Six Sigma’s data-driven quest to achieve continuous improvement. As such, companies that put Lean Six Sigma methods into their business process improvement plans aim to eliminate waste and defects while improving performance and standardizing processes.
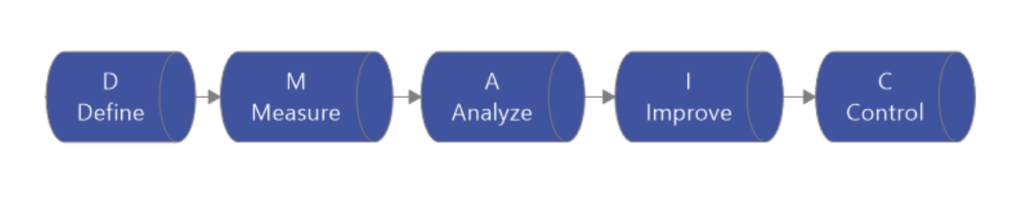
The foundation of your business process improvement plan using the Lean Six Sigma methodology is a five-step method called DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve, and control):
- Define the problem.
- Measure (quantify) the problem using numbers or supporting data.
- Analyze and identify the underlying cause of the problem.
- Improve the process by implementing solutions to resolve the root causes of the problem.
- Control the process strategy to generate sustainable improvement.
Here is an example of what a Lean Six Sigma business process improvement workflow might look like in MindManager:
Kaizen
By continuously monitoring, identifying, and implementing improvements, the Kaizen methodology powers ongoing positive progress for business processes. This approach uses small, ongoing changes that build up to significant improvements over time.
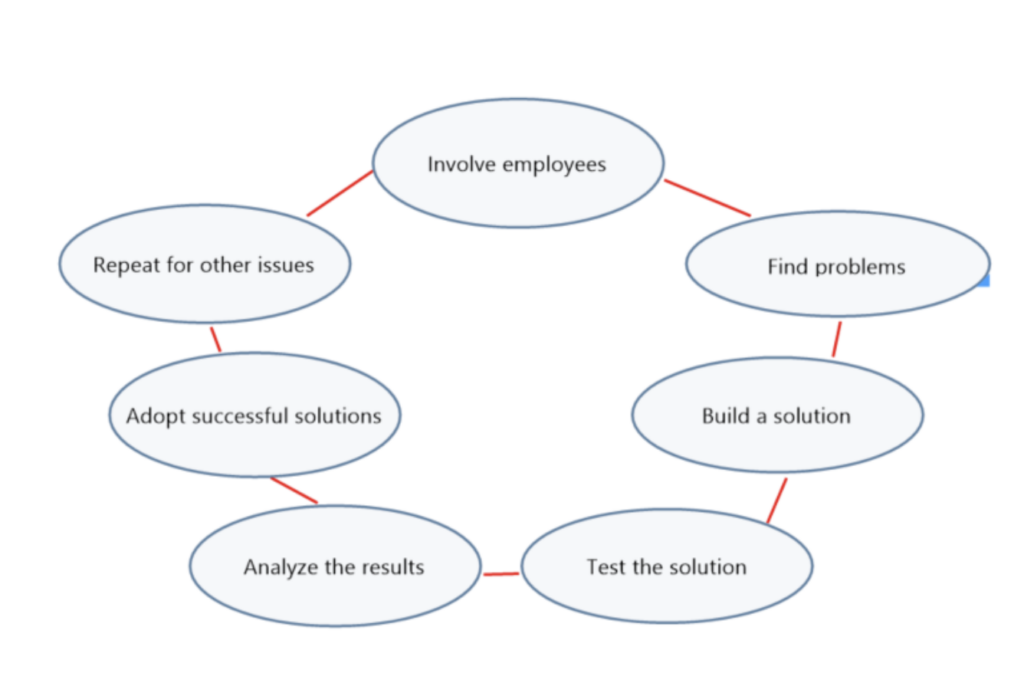
Kaizen takes a bottom-up approach to process improvement by encouraging all employees to suggest and implement BPI strategies as they see opportunities to do so. While there are numerous Kaizen frameworks you can use, this method is typically implemented by following a six-step cycle for continuous improvement:
- Get employees involved. Involve employees in discussions about problems, improvements, and general information gathering.
- Create a problem inventory. Using the feedback obtained from employee discussions, review current processes, define any problems, and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Develop a solution. Encourage creative ideas from all employees and select the solution that will best remedy process gaps.
- Test the change. Take small steps to test out the BPI solution, such as pilot programs and other opportunities for team members to participate in the rollout.
- Analyze the results. Assess your progress towards improving the process. If the change is successful, you can apply the BPI strategy to other processes in your organization. Otherwise, adjust as necessary.
- Repeat. Repeat the Kaizen process on an ongoing basis to identify and address new issues to further enhance your organization’s business processes.
Eliminating bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and redundant tasks using business process improvement will help improve workflows and enhance the employee experience. For a BPI strategy or initiative to be successful, it is important to both document and communicate processes for everyone in the organization. Doing so helps to reduce ambiguity and ensures that you avoid regression into previous behaviors and practices that do not support your business process improvements.
Your business process improvement plan is unique to your particular needs, so accordingly MindManager offers an array of customizable templates as well the ability to build your own diagrams from scratch. Furthermore, MindManager makes it simple to collaborate on your BPI plans thanks to real-time, cross-platform co-editing capabilities.
Discover how MindManager can help you with business process improvement.

