Artificial intelligence is changing the way people write, work, pay their bills, and interact with each other.
One of the most exciting applications of AI is in natural language processing (NLP).
NLP is the ability of computers to understand, analyze, and manipulate human language.
Tools like IBM Watson allow users to train, tune, and distribute models with generative AI and machine learning capabilities.
These tools enable computers (and, therefore, humans) to understand the overarching themes and sentiments in vast amounts of data.
The core challenge of using these applications is that they generate complex information that is difficult to implement into actionable insights.
Jose Maria Guerrero, an AI specialist and author, is dedicated to overcoming that challenge and helping people better use semantic analysis in NLP. His solution? Using mind mapping to organize and visualize that data.
Streamline semantic analysis NLP, get your free trial of MindManager today!
What exactly is semantic analysis in NLP?
Semantic analysis in NLP is the process of understanding the meaning and context of human language.
The simplest example of semantic analysis is something you likely do every day — typing a query into a search engine.
Let’s say you type in the word “cowboys” into Google. From that single word, Google tries to figure out what you mean — are you looking for a bike, boots, or scores from last night’s game?
The search results will be a mix of all the options since there is no additional context.
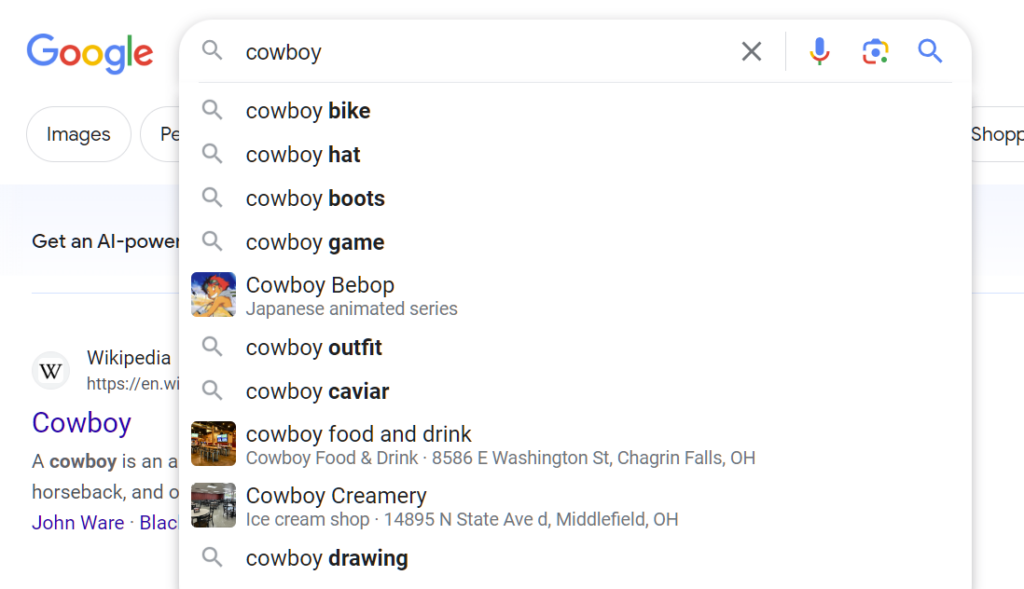
Now, let’s say you search for “cowboy boots.” Using semantic analysis, Google can connect the words “cowboy” and “boots” to realize you’re looking for a specific type of shoe.
Here’s a look at what those search results look like:

Semantic analysis in the context of NLP is a bit more complicated.
Models can analyze thousands of pages of text. However, even the more complex models use a similar strategy to understand how words relate to each other and provide context.
Semantic analysis in NLP is about extracting the deeper meaning and relationships between words, enabling machines to comprehend and work with human language in a more meaningful way.
What are the key challenges in semantic analysis today?
Traditional methods for performing semantic analysis make it hard for people to work efficiently. In most cases, the content is delivered as linear text or in a website format. Trying to understand all that information is challenging, as there is too much information to visualize as linear text.
Say a software company wants to understand how customers feel about their product. They gather vast amounts of data from social media, blogs, articles, emails, surveys, documents, and internal chats.
Using semantic analysis, they try to understand how their customers feel about their brand and specific products.
Trying to turn that data into actionable insights is complicated because there is too much data to get a good feel for the overarching sentiment.
That is where mind mapping comes in.
How does MindManager help improve semantic analysis?
Jose Maria Guerrero developed a technique that uses automation to turn the results from IBM Watson into mind maps. This makes it easier to understand large amounts of text.
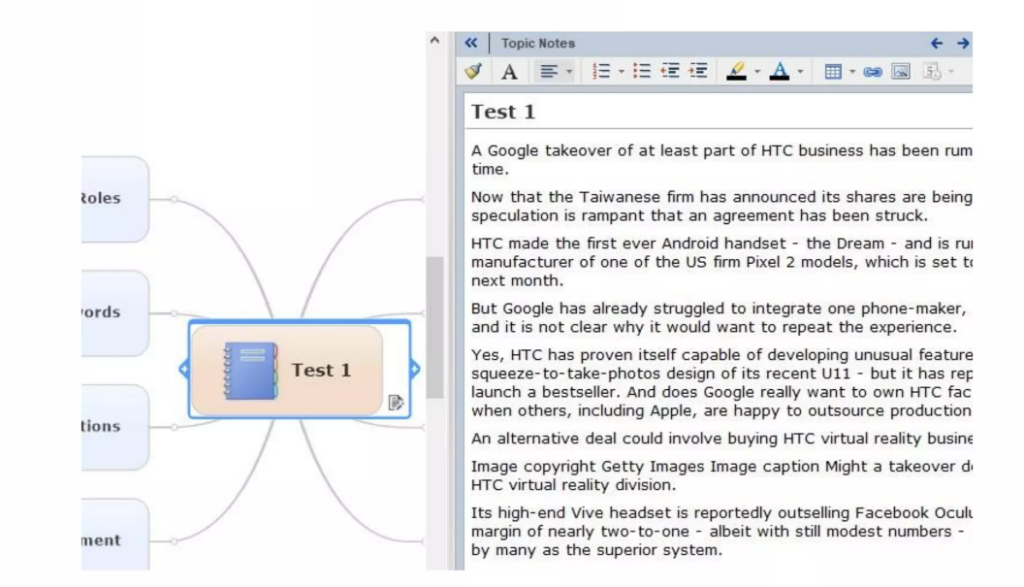
Here’s an example of how it looks in practice:
Using MindManager for visualizing NLP semantic analysis results makes it easier to understand relationships between data by sorting the text into topics.
The visual aspect is easier for users to navigate and helps them see the larger picture.
The source text, code, or other details can be added, allowing users to dig in deeper if needed:
So, mind mapping allows users to zero in on the data that matters most to their application.
For example, if the mind map breaks topics down by specific products a company offers, the product team could focus on the sentiment related to each specific product line.
Mind maps can also be used to explore semantic roles in text:
Semantic roles refer to the specific function words or phrases play within a linguistic context. These roles identify the relationships between the elements of a sentence and provide context about who or what is doing an action, receiving it, or being affected by it.
Understanding semantic roles is crucial to understanding the meaning of a sentence.
As more applications of AI are developed, the need for improved visualization of the information generated will increase exponentially, making mind mapping an integral part of the growing AI sector.
Learn more about how MindManager can be used in the context of AI
While MindManager does not use AI or automation on its own, it does have applications in the AI world. For example, mind maps can help create structured documents that include project overviews, code, experiment results, and marketing plans in one place.
Mind maps can also be helpful in explaining complex topics related to AI, such as algorithms or long-term projects.
The future of AI is a work in progress, but MindManager has applications that go beyond brainstorming.
Streamline semantic analysis NLP, get your free trial of MindManager today!
Are you interested in learning more about AI and mind mapping? Check out Jose Maria Guerrero’s book Mind Mapping and Artificial Intelligence.

